Architecture Overview
Overview
lakeFS is distributed as a single binary encapsulating several logical services:
The server itself is stateless, meaning you can easily add more instances to handle bigger load.
lakeFS stores data in an underlying S3 bucket with some of its metadata stored in PostgreSQL. (see Data Model)
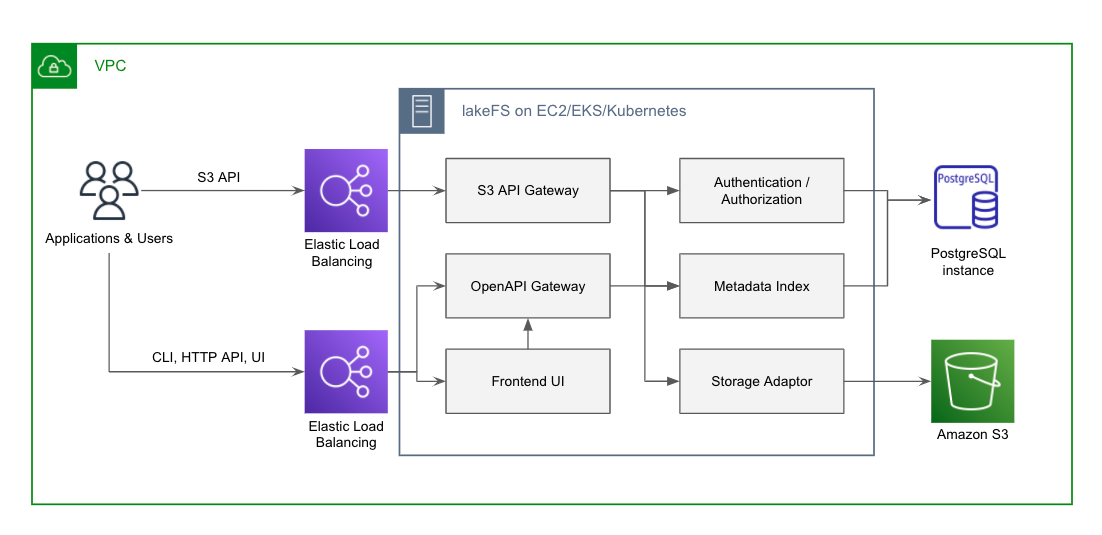
lakeFS Components
S3 Gateway
The API Gateway implements lakeFS’ compatibility with S3. It implements a compatible subset of the S3 API to ensure most data systems can use lakeFS as a drop-in replacement for S3.
To achieve this, the gateway exposes an HTTP listener on a dedicated host and port.
See the S3 API Reference section for information on supported API operations.
OpenAPI Server
The Swagger (OpenAPI) Server exposes the full set of lakeFS operations (see Reference). This includes basic CRUD operations against repositories and objects, as well as versioning related operations such as branching, merging, committing and reverting changes to data.
S3 Storage Adapter
The S3 Storage Adapter is the component in charge of communication with the underlying S3 bucket. It is logically decoupled from the S3 Gateway to allow for future compatibility with other types of underlying storage such as HDFS or S3-Compatible storage providers.
See the roadmap for information on future plans for storage compatibility.
Metadata Index
To learn about the data model used to store lakeFS metadata, see the data model section.
Authentication & Authorization Service
The Auth service handles creation, management and validation of user credentials and RBAC policies.
The credential scheme, along with the request signing logic are compatible with AWS IAM (both SIGv2 and SIGv4).
Currently, the auth service manages its own database of users and credentials and does not use IAM in any way.
Frontend UI
The UI layer is a simple browser-based client that uses the OpenAPI server. It allows management, exploration and data access to repositories, branches, commits and objects in the system.