Configurable Hooks
Like other version control systems, lakeFS allows the configuration of Actions to trigger when predefined events occur.
Supported Events:
pre_commit- Action runs when the commit occurs, before the commit is finalized.post_commit- Action runs after the commit is finalized.pre_merge- Action runs when the merge occurs, before the merge is finalized.post_merge- Action runs after the merge is finalized.
lakeFS Actions are handled per repository and cannot be shared between repositories.
Failure of any Hook under any Action of a pre_* event will result in aborting the lakeFS operation that is taking place.
On the contrary, Hook failures under any Action of a post_* event will not affect the same operation.
Hooks are managed by Action files that are written to a prefix in the lakeFS repository.
This allows configuration-as-code inside lakeFS, where Action files are declarative and written in YAML.
Example use-cases
- Format Validator: A webhook that checks new files to ensure they are of a set of allowed data format.
- Schema Validator: A webhook that reads new Parquet and ORC files to ensure they don’t contain a block list of column names (or name prefixes). This is useful when we want to avoid accidental PII exposure.
For more examples and configuration samples, check out lakeFS-hooks example repo.
Terminology
Action
An Action is a list of Hooks with the same trigger configuration, i.e. an event will trigger all Hooks under an Action, or none at all.
The Hooks under an Action are ordered and so is their execution. A Hook will only be executed if all previous Hooks that were triggered with it, had passed.
Hook
A Hook is the basic building block of an Action.
Failure of a single Hook will stop the execution of the containing Action and fail the Run.
Action file
Schema of the Action file:
| Property | Description | Data Type | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | Identify the Action file | String | false | If missing, filename is used instead |
| on | List of events that will trigger the hooks | List | true | |
| on |
Glob pattern list of branches that triggers the hooks | List | false | If empty, Action runs on all branches |
| hooks | List of hooks to be executed | List | true | |
| hook.id | ID of the hook, must be unique within the Action |
String | true | |
| hook.type | Type of the hook (currently only webhook supported |
String | true | |
| hook.properties | Hook’s specific configuration | Dictionary | true |
Example:
name: Good files check
description: set of checks to verify that branch is good
on:
pre-commit:
pre-merge:
branches:
- main
hooks:
- id: no_temp
type: webhook
description: checking no temporary files found
properties:
url: "https://your.domain.io/webhook?notmp=true?t=1za2PbkZK1bd4prMuTDr6BeEQwWYcX2R"
- id: no_freeze
type: webhook
description: check production is not in dev freeze
properties:
url: "https://your.domain.io/webhook?nofreeze=true?t=1za2PbkZK1bd4prMuTDr6BeEQwWYcX2R"
Note: lakeFS will validate action files only when an Event occurred.
Use lakectl actions validate <path> to validate your action files locally.
Run
A Run is an instantiation of the repository’s Action files when the triggering event occurs.
For example, if our repository contains a pre-commit hook, every commit would generate a Run for that specific commit.
lakeFS will fetch, parse and filter the repository Action files and start to execute the Hooks under each Action.
All executed Hooks (each with hook_run_id) exists in the context of that Run (run_id).
Uploading Action files
Action files should be uploaded with the prefix _lakefs_actions/ to the lakeFS repository.
When an actionable event (see Supported Events above) takes place, lakeFS will read all files with prefix _lakefs_actions/
in the repository branch where the action occurred.
A failure to parse an Action file will result with a failing Run.
For example, lakeFS will search and execute all matching Action files with the prefix lakefs://repo1/feature-1/_lakefs_actions/ on:
- Commit to
feature-1branch onrepo1repository. - Merge to
mainbranch fromfeature-1branch onrepo1repository.
Runs API & CLI
OpenAPI endpoint and lakectl expose the results of Runs execution per repository, branch, commit and specific Action.
The endpoint also allows to download the execution log of any executed Hook under each Run for observability.
Result Files
There are 2 types of files that are stored in the metadata section of lakeFS repository with each Run:
_lakefs/actions/log/<runID>/<hookRunID>.log- Execution log of the specificHookrun._lakefs/actions/log/<runID>/run.manifest- Manifest with allHooksexecution for the run with their results and additional metadata.
Note: Metadata section of a lakeFS repository is where lakeFS keeps its metadata, like commits and metaranges. Metadata files stored in the metadata section aren’t accessible like user stored files.
Hook types
Currently, there are two types of Hooks that are supported by lakeFS: Webhook and Airflow.
Webhooks
A Webhook is a Hook type that sends an HTTP POST request to the configured URL.
Any non 2XX response by the responding endpoint will fail the Hook, cancel the execution of the following Hooks
under the same Action. For pre_* hooks, the triggering operation (commit/merge) will also be aborted.
Warning: You should not use pre_* webhooks for long-running tasks, since they block the performed operation.
Moreover, the branch is locked during the execution of pre_* hooks, so the webhook server cannot perform any write operations (like uploading or commits) on the branch.
Action file Webhook properties
| Property | Description | Data Type | Required | Default Value | Env Vars Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| url | The URL address of the request | String | true | no | |
| timeout | Time to wait for response before failing the hook | String (golang’s Duration representation) | false | 1m | no |
| query_params | List of query params that will be added to the request | Dictionary(String:String or String:List(String) | false | yes | |
| headers | List of query params that will be added to the request | Dictionary(String:String) | false | yes |
Secrets & Environment Variables
lakeFS Actions supports secrets by using environment variables.
The following format {{ ENV.SOME_ENV_VAR }} will be replaced with the value of SOME_ENV_VAR
during the execution of the action. If that environment variable doesn’t exist in the lakeFS server environment, the action run will fail.
Example:
...
hooks:
- id: prevent_user_columns
type: webhook
description: Ensure no user_* columns under public/
properties:
url: "http://<host:port>/webhooks/schema"
timeout: 1m30s
query_params:
disallow: ["user_", "private_"]
prefix: public/
headers:
secret_header: "{{ ENV.MY_SECRET }}"
...
Request body schema
Upon execution, a webhook will send a request containing a JSON object with the following fields:
| Field | Description | Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventType | Type of the event that triggered the Action |
string | pre_commit |
| EventTime | Time of the event that triggered the Action (RFC3339) |
string | 2006-01-02T15:04:05Z07:00 |
| ActionName | Containing Hook Action’s Name |
string | |
| HookID | ID of the Hook |
string | |
| RepositoryID | ID of the Repository | string | |
| BranchID | ID of the Branch | string | |
| SourceRef | Reference to the source that triggered the event (source Branch for commit or merge) | string | |
| CommitMessage | The message for the commit (or merge) that is taking place | string | |
| Committer | Name of the committer | string | |
| CommitMetadata | The metadata for the commit that is taking place | string |
Example:
{
"event_type": "pre-merge",
"event_time": "2021-02-28T14:03:31Z",
"action_name": "test action",
"hook_id": "prevent_user_columns",
"repository_id": "repo1",
"branch_id": "feature-1",
"source_ref": "feature-1",
"commit_message": "merge commit message",
"committer": "committer",
"commit_metadata": {
"key": "value"
}
}
Airflow Hooks
Airflow Hook triggers a DAG run in an Airflow installation using Airflow’s REST API. The hook run succeeds if the DAG was triggered, and fails otherwise.
Action file Airflow hook properties
| Property | Description | Data Type | Example | Required | Env Vars Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| url | The URL of the Airflow instance | String | “http://localhost:8080” | true | no |
| dag_id | The DAG to trigger | String | “example_dag” | true | no |
| username | The name of the Airflow user performing the request | String | “admin” | true | no |
| password | The password of the Airflow user performing the request | String | “admin” | true | yes |
| dag_conf | DAG run configuration that will be passed as is | JSON | false | no |
Example:
...
hooks:
- id: trigger_my_dag
type: airflow
description: Trigger an example_dag
properties:
url: "http://localhost:8000"
dag_id: "example_dag"
username: "admin"
password: "{{ ENV.AIRFLOW_SECRET }}"
dag_conf:
some: "additional_conf"
...
Hook Record in configuration field
lakeFS will add an entry to the Airflow request configuration property (conf) with the event that triggered the action.
The key of the record will be lakeFS_event and the value will match the one described here
Experimentation
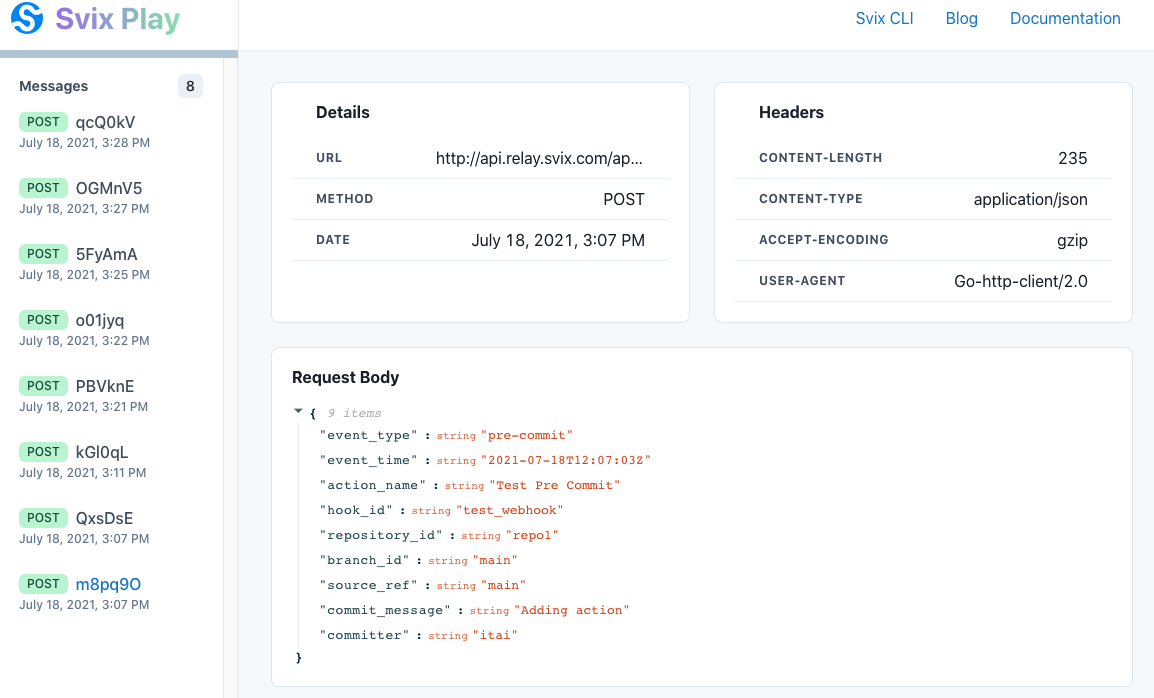
It’s sometimes easier to start experimenting with lakeFS webhooks, even before you have a running server to receive the calls. There are a couple of online tools that can intercept and display the webhook requests, one of them is Svix.
-
Go to play.svix.com and copy the URL address supplied by Svix. It should look like
https://api.relay.svix.com/api/v1/play/receive/<Random_Gen_String>/ -
Upload the following action file to lakeFS under the path
_lakefs_actions/test.yamlin the default branch:name: Sending everything to Svix description: Experimenting with webhooks on: pre-commit: branches: pre-merge: branches: post-commit: branches: post-merge: branches: hooks: - id: svix type: webhook properties: url: "https://api.relay.svix.com/api/v1/play/receive/<Random_Gen_String>/"by using:
lakectl fs upload lakefs://example-repo/main/_lakefs_actions/test.yaml -s path/to/action/fileor the UI.
-
Commit that file to the branch.
lakectl commit lakefs://example-repo/main -m 'added webhook action file' -
Every time you commit or merge to a branch, the relevant
pre_*andpost_*requests will be available in the Svix endpoint you provided. You can also check theActionstab in the lakeFS UI for more details.